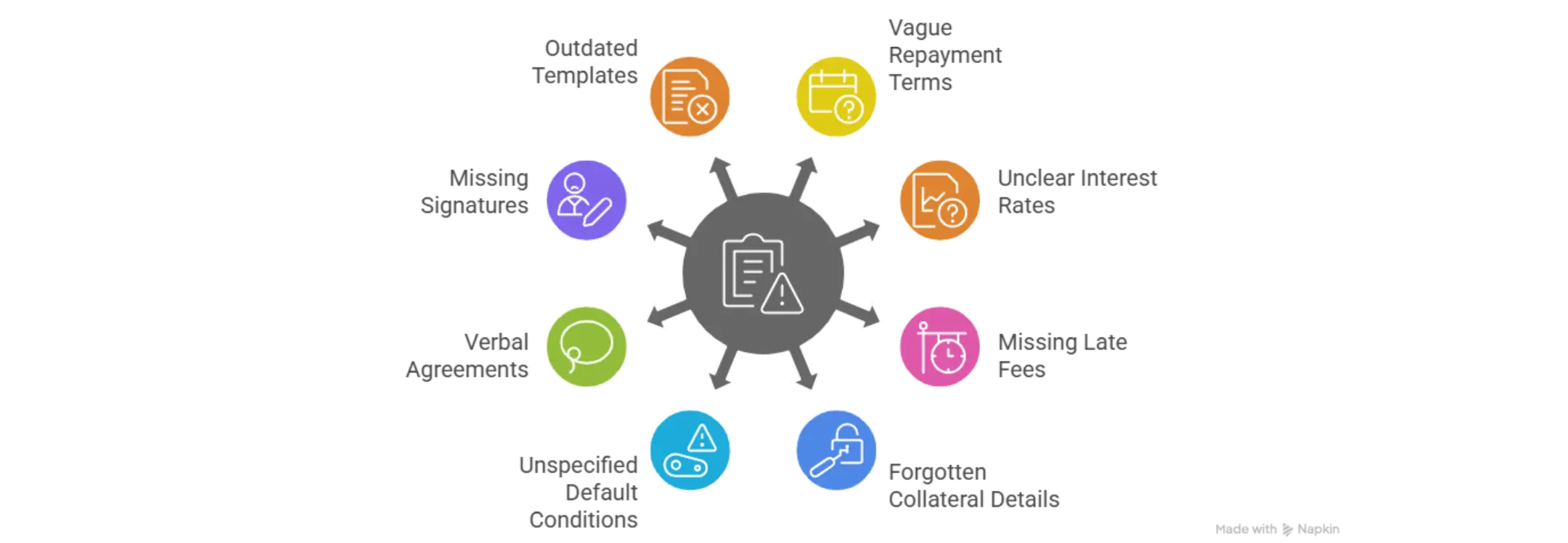
TL;DR- Vague or missing repayment terms create confusion about when payments are due, triggering disputes if borrowers claim unclear requirements about payment dates or schedules
- Missing interest rate details prevent enforcement and create disputes about whether interest is simple or compound and whether rates are annual or monthly
- Not defining late fees or penalties weakens enforcement because courts cannot determine what consequences apply if payments are delayed beyond agreed dates
- Forgetting collateral details when securing loans prevents clear identification of what property secures the obligation and what happens if the borrower defaults
- Not specifying default conditions leaves ambiguity about what actions constitute default, making it difficult to enforce remedies when borrowers breach the note
- Relying on verbal agreements instead of writing creates he-said-she-said disputes with no documentation proving what was actually agreed upon between parties
- Missing signatures or dates invalidates promissory notes because unsigned documents lack proof that both parties actually agreed to loan terms
- Using outdated templates omits current legal requirements, state-specific provisions, and critical clauses needed for modern loan enforcement
- Ziji Legal Forms provides comprehensive promissory note templates that prevent these critical mistakes while ensuring all legal requirements are included
Introduction: Why Promissory Note Accuracy Matters
A promissory note is a written promise to repay a specific loan amount under defined terms. Despite appearing simple, promissory notes require precise language and complete information to remain legally binding and enforceable when disputes arise.
Missing or vague promissory note terms create the exact problems the document was designed to prevent. Lenders cannot collect debts without clear evidence of payment obligations, while borrowers face uncertainty about what they actually owe. Understanding common mistakes and how to avoid them protects both parties while ensuring loan enforceability.
Mistake 1: Leaving Repayment Terms Vague or Missing
Why Clear Due Dates Matter
Vague repayment language like "repay when convenient" or "pay back soon" creates impossible disputes about when payments actually are due. Without specific due dates, neither party can determine whether the borrower has actually defaulted or simply misunderstood payment timing.
Clear repayment schedules specify exact payment dates, amounts due on each date, and how many total payments comprise the complete loan repayment. Specific language like "monthly payments of $500 on the fifteenth of each month for 24 months" leaves no ambiguity about obligations.
Impact on Enforcement
Courts cannot enforce vague repayment terms because they cannot determine what the parties actually agreed to. If a case goes to court, judges require clear, unambiguous language establishing exactly when payments are due and in what amounts.
Borrowers facing enforcement action can argue that repayment terms were unclear and that they were complying with reasonable interpretation of flexible language. Clear, specific terms eliminate these enforcement challenges.
Essential Repayment Information
Promissory notes should specify the total loan amount, whether payments are made in installments or as lump sum repayment, exact payment due dates, payment amounts or formula for calculating amounts, location where payments should be sent, and person or entity to receive payments.
Mistake 2: Missing or Unclear Interest Rate Details
Why Interest Terms Must Be Specific
Undefined or ambiguous interest rates prevent lenders from calculating what borrowers actually owe over the loan period. Courts cannot enforce loans when interest terms are unclear because they cannot determine the correct repayment amounts.
Interest rate specifications must clarify whether interest is simple or compound, whether rates are expressed annually or monthly, and whether rates remain fixed or change under specific circumstances. Some lenders forget that even zero-interest loans should state explicitly that no interest applies.
Calculating Interest Disputes
Without clear interest rate specifications, lenders and borrowers dispute how much interest accrued and what total amounts are owed. These disputes become especially contentious when interest compounds or when rates change based on payment status.
IRS rules require that family loans include minimum interest rates to avoid tax consequences. Using insufficient rates can trigger unexpected tax liability regardless of what parties actually intended.
Required Interest Specifications
Promissory notes must state interest rate as a percentage, specify whether rates are annual or monthly percentages, clarify whether interest is simple or compound, and state when interest begins accruing. Notes should also specify what happens to interest if the borrower makes early payments or if payments are late.
Mistake 3: Not Defining Late Fees or Penalty Terms
How Missing Penalties Weaken Enforcement
Absent late fee provisions prevent lenders from imposing financial consequences when borrowers miss payment deadlines. Without documented late fees, lenders cannot recover costs associated with late payments or pursue collection remedies based on contractual penalties.
Late fee specifications provide financial incentive for borrowers to make timely payments while establishing enforceable remedies available to lenders if payments are delayed. Clear penalties deter delinquency and provide compensation when it occurs despite warnings.
Default Interest and Acceleration Clauses
Beyond simple late fees, promissory notes should specify whether interest rates increase if payments are missed, whether missed payments trigger default interest on the entire loan balance, and whether missed payments allow lenders to demand immediate repayment of all remaining balances.
These provisions encourage timely payment while establishing rights available to lenders if borrowers breach payment obligations. Clear specifications prevent disputes about what remedies apply when defaults occur.
Reasonable Penalty Requirements
Late fees must be reasonable and not excessive enough to be considered penalties that courts would refuse to enforce. Typical late fees range from two to five percent of missed payment amounts, though this varies by jurisdiction and loan type.
Mistake 4: Forgetting Collateral Details or Description
When Collateral Should Be Included
Secured loans requiring collateral must clearly describe what property secures the obligation and what happens if the borrower defaults. Unclear collateral descriptions prevent lenders from seizing property when borrowers refuse to repay.
Collateral descriptions must be specific enough that both parties clearly understand what property is pledged and distinctive enough to identify exact items rather than general categories. Vague descriptions like "personal property" or "household items" create disputes about what can actually be seized.
Risks of Unclear Collateral
Without clear collateral specifications, lenders struggle to enforce security interests or seize property if borrowers default. Other creditors might claim superior rights to the same collateral if documentation is unclear about what was pledged.
Borrowers can dispute that specific items were actually part of the collateral agreement if descriptions are vague. This uncertainty prevents effective collection through collateral seizure and liquidation.
Complete Collateral Information
Promissory notes should describe collateral with specificity including item type, model, serial numbers if applicable, condition at time of pledge, and storage location. Notes should clarify whether collateral includes insurance proceeds and who holds title during the loan period.
Mistake 5: Not Specifying What Constitutes Default
Ambiguity About Default Conditions
Undefined default provisions create disputes about when borrowers have actually breached the note and triggered lender remedies. Without clear definitions, borrowers can argue they have not defaulted despite missing payments or violating other conditions.
Default occurs when borrowers fail to meet obligations specified in promissory notes. Clear default provisions specify missed payments, failure to maintain collateral, violation of other contractual conditions, and insolvency or bankruptcy as automatic default triggers.
Enforcement Challenges
Courts cannot enforce remedies tied to default if the promissory note does not clearly establish what constitutes default. Lenders without clear default specifications struggle to obtain judgments even when borrowers obviously have breached basic payment obligations.
Default provisions should specify whether single missed payments constitute default or whether grace periods apply. They should clarify whether subsequent breaches have cumulative effect triggering acceleration clauses.
Essential Default Language
Promissory notes should state that missing any payment constitutes default, specify any grace periods provided before default occurs, clarify whether partial payments cure default, identify other conduct constituting default, and specify what lender remedies are available upon default.
Mistake 6: Relying on Verbal Agreements Instead of Written Documentation
Problems Without Written Records
Verbal loan agreements create impossible disputes about what was actually promised because one party's word stands against the other with no objective evidence. Years later, memories fade and parties dispute whether certain terms were ever discussed.
Written promissory notes create objective evidence proving what both parties agreed to regarding repayment amounts, interest rates, payment dates, collateral, and default provisions. This written record prevents misunderstandings and provides courtroom evidence of actual agreements.
Legal Enforceability Requirements
Courts strongly prefer written evidence proving loan terms. Verbal agreements may be enforceable in some situations, but written promissory notes provide irrefutable proof of what was agreed and eliminate disputes about payment obligations.
Federal law and many state laws require written promissory notes for certain transaction types. Even when not legally required, written notes provide essential protection against disputes.
Benefits of Written Documentation
Written promissory notes create permanent records proving loan existence, establish clear payment obligations, document agreed interest and penalty terms, identify collateral if applicable, and provide evidence for court enforcement if disputes arise.
Mistake 7: Not Getting Both Party Signatures or Leaving Notes Undated
Why Signatures Are Essential
Unsigned promissory notes lack legal validity because they do not demonstrate that both parties actually agreed to documented terms. Unsigned documents can be disputed as fabricated or amended without authorization.
Both the borrower and lender should sign promissory notes, preferably with printed names and dates alongside signatures. Dated signatures establish when agreements were made and provide temporal reference if statute of limitations questions later arise.
Problems Caused by Unsigned Notes
Unsigned or partially signed notes cannot be enforced in court because judges cannot determine whether both parties actually intended to be bound. Courts require evidence that borrowers knowingly agreed to documented obligations.
Lenders with unsigned notes face impossible collection challenges because they cannot prove that borrowers agreed to repay. Borrowers can deny the entire debt or claim the note was forged or fraudulently altered.
Proper Signature Procedures
Both borrower and lender should print their full legal names below their signatures. Dates should appear next to signatures establishing when parties agreed to note terms. Some situations benefit from witness signatures or notary authentication adding additional verification.
Mistake 8: Using Outdated or Incomplete Templates
Problems with Generic Forms
Outdated promissory note templates may lack provisions required by current law, omit state-specific language, or fail to address modern loan situations like electronic payments or cryptocurrency transactions. Generic forms designed for general situations miss industry-specific requirements.
Templates created years ago may not reflect legal changes affecting promissory note enforceability, interest rate limits, or required disclosure provisions. Modern templates incorporate current legal standards ensuring notes remain enforceable.
Missing Critical Clauses
Outdated templates may omit acceleration clauses allowing immediate repayment demands if defaults occur, lack default interest provisions increasing rates if payments are missed, omit collateral descriptions needed for secured loans, or fail to include representations and warranties protecting lenders.
Using incomplete templates creates gaps in protection that become apparent only when disputes arise or enforcement becomes necessary. Missing provisions that could have prevented litigation may be irrecoverable once problems develop.
Selecting Current Templates
Use promissory note templates specifically created for current year that reflect your jurisdiction's legal requirements. Verify templates include all standard provisions and address your specific loan situation including whether loans are secured or unsecured, whether interest is involved, and what payment structure applies.
Ziji Legal Forms provides promissory note templates that are vetted by legal professionals and continuously updated based on current regulations.
How to Create a Promissory Note Using Ziji Legal Forms
1. Choose template
Access Ziji Legal Forms' Financial section and select the Promissory Note Template designed to include all essential loan terms and legal requirements.
2. Add Parties' Details
Enter the borrower's full legal name, address, and contact information along with the lender's complete information to clearly identify all parties to the loan agreement.
3. Add The Terms
Specify the loan amount, interest rate with clarification about whether interest is simple or compound and whether rates are annual or monthly, payment schedule with specific due dates and amounts, late fees or default interest provisions, and any collateral pledged to secure the loan.
4. Add Final Details
Include default conditions specifying what constitutes breach, acceleration clauses allowing demand for full repayment upon default, representations and warranties from both parties, governing law specification, and dispute resolution procedures.
5. Preview and print.
Review the completed promissory note thoroughly to verify all information is accurate and complete, then download in PDF or Word format for signature by both parties with dates and printed names.
Using Ziji Templates Reduces Common Mistakes
Ziji Legal Forms ensures specific repayment terms by requiring exact payment dates and amounts rather than vague language. Templates automatically include interest rate specifications clarifying calculation methods and annual or monthly percentages. Pre-built late fee and default interest provisions prevent omissions of critical penalty language. Collateral description fields guide users toward specific identification rather than vague references. Default condition sections specify what constitutes breach and what lender remedies apply. Signature and date fields remind users that unsigned notes lack enforceability. Current templates reflect all legal requirements and state-specific provisions.
Conclusion: Protect Your Loan with Complete and Accurate Promissory Notes
Comprehensive promissory notes with clear repayment terms, interest specifications, penalty provisions, and default conditions protect both lenders and borrowers while ensuring legal enforceability. Using Ziji Legal Forms' professionally designed templates eliminates the most common drafting errors while ensuring all legal requirements and loan protections are properly included.
Promissory Note FAQs
What is a promissory note also known as?
A promissory note is also known as the following: demand note, IOU “I owe you”, loan agreement, or promise to pay agreement.
What is a promissory note?
A promissory note is a legal instrument where the borrower promises to repay the loan owed to the lender under the terms of the note. It’s essentially a promise to repay the lender.
Who is a co-signer for the promissory note?
The co-signer, also called a guarantor, is someone who is guaranteeing the loan and will be responsible for paying for the full amount of the loan if the borrower cannot repay the loan to the lender.
What should the promissory note cover?
The promissory note typically contains the following terms:
- the original loan amount
- interest payment, if any
- repayment schedule
- late fees, if any
- collateral for the loan, if any
You can use our template and create a promissory note with the following steps:
- Select the loan’s location
This is the state where the lender lives and the promissory note will be customized to that jurisdiction.
- List the parties to the loan
Provide the names and addresses of the lender and the borrower. You may also include a co-signer or guarantor if there is one.
- List the terms of the loan
Describe how much is the loan amount. Secondly, is interest being charged? If so, what percentage will the interest be and how will the interest be calculated and accrued. Thirdly, list the repayment schedule. Typically, loans are repaid in instalments and payments can be made weekly, monthly, quarterly, semi-annually or yearly. However, the loan can also be repaid in one lump sum, or at a later date based on the lender’s demand. You will also need to list the first and final payment date to the loan repayment schedule.
- List the prepayment teams
Loans can have prepayment penalty if the borrower repays it early because most lenders are interested in earning the most interest with the loan. You can decide whether to have a prepayment penalty in customizing this promissory note.
- Collateral
A collateral is an asset the lender accepts as security for a loan in case the borrower fails to repay the loan. This is typically reserved for risky borrowers that may not be as credit worthy and who tries to borrow a substantial amount of money. For example, the borrower can use a car, or jewellery as collateral and upon default of the loan, the lender can go to small claims court to seize the collateral or other assets from the borrower in order to satisfy the failure of repayment.
If there is collateral to the loan, describe the collateral in detail to ensure there is no ambiguity what property is being used as collateral. For example, listing the year, make and model of the car, along with the VIN number. If it’s a piece of electronics, list the serial number etc.
Do I need to notarize my promissory note?
You only need the signature of the lender and borrower to have an enforceable promissory note. However having a notary to witness the document adds another layer of authenticity and protection in case the loan gets disputed in court in the future. For loans involving substantial amount of money, it may be prudent to have it notarized.
Can a promissory note be modified after it is signed?
Yes, a promissory note can be changed or amended if both the lender and borrower agree to the new terms. Any modifications should be documented in writing and signed by both parties to avoid confusion or disputes later on.
What happens if the borrower misses a payment?
If the borrower fails to make a scheduled payment, the lender may charge late fees if specified in the note. Repeated missed payments could lead to default, giving the lender the right to demand the full remaining balance immediately or take legal action to recover the debt.
Is interest always required on a promissory note?
No, interest is not mandatory on a promissory note. Some loans may be interest-free, especially between family or friends. However, if interest is charged, the note should clearly state the interest rate and how it will be calculated.
What is the difference between a secured and unsecured promissory note?
A secured promissory note is backed by collateral, meaning the lender can seize specific assets if the borrower defaults. An unsecured promissory note has no collateral backing, so the lender’s remedy is limited to suing the borrower for repayment.
Can a promissory note be transferred to someone else?
Yes, promissory notes can sometimes be assigned or sold to a third party. This means the new holder of the note can collect payments instead of the original lender. The transfer should be documented properly to ensure the borrower knows who to pay.
What jurisdictions can use our promissory note?
You can use our template to create a legal and valid promissory note for the following jurisdictions:
|
Alabama
Alaska
Arizona
Arkansas
California
Colorado
Connecticut
Delaware
District of Columbia
Florida
Georgia
Hawaii
Idaho
Illinois
Indiana
Iowa
Kansas
Kentucky
Louisiana
Maine
Maryland
Massachusetts
Michigan
Minnesota
Mississippi
Missouri
Montana
Nebraska
Nevada
New Hampshire
New Jersey
New Mexico
New York
North Carolina
North Dakota
Ohio
Oklahoma
Oregon
Pennsylvania
Rhode Island
South Carolina
South Dakota
Tennessee
Texas
Utah
Vermont
Virginia
Washington
West Virginia
Wisconsin
Wyoming |
AL
AK
AZ
AR
CA
CO
CT
DE
DC
FL
GA
HI
ID
IL
IN
IA
KS
KY
LA
ME
MD
MA
MI
MN
MS
MO
MT
NE
NV
NH
NJ
NM
NY
NC
ND
OH
OK
OR
PA
RI
SC
SD
TN
TX
UT
VT
VA
WA
WV
WI
WY |